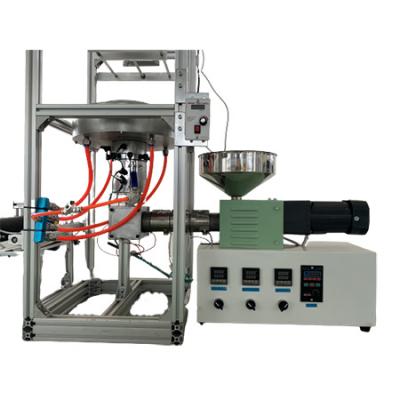
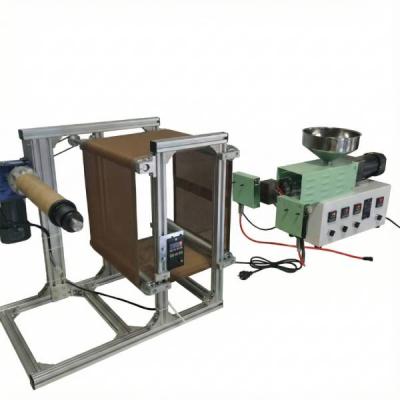
Desktop Film Calendering and Film Blowing
Film Blowing
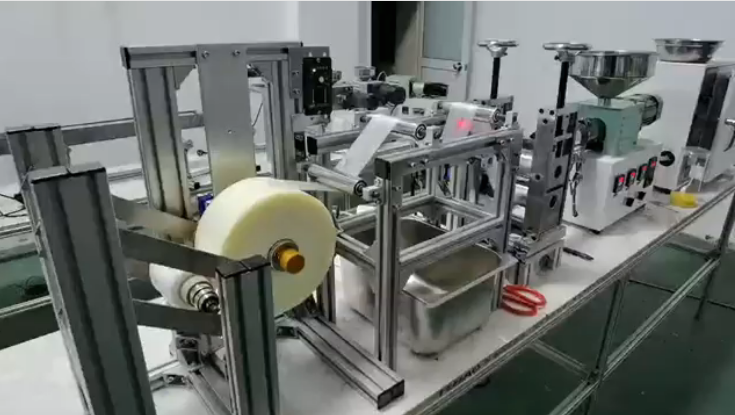
If you are working on plastic compounding, and want to find out if it fits for film blown, this desktop film-blown experimental production line is just suitable for the project. Because the desktop SJ35 extruder won't waste many plastic pellets for experimental purposes.
Film blowing is a process used to produce plastic films of various thicknesses and widths, typically for use in packaging, agriculture, construction, and other industries. The process involves melting a polymer resin, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, and extruding it through a circular die to form a tube of molten polymer. The tube is then inflated with air to expand it into a bubble, which is cooled by air or water and then collapsed into a thin film as it exits the extrusion process.
During the process, the thickness of the film is controlled by the size of the die, the air pressure inside the bubble, and the speed at which the bubble is inflated. The properties of the film, such as its tensile strength, tear resistance, and optical clarity, are affected by the type of polymer resin, the processing conditions, and any additives or fillers that are used.
Film blowing is a versatile method that can produce films with a wide range of properties and applications, from thin, flexible packaging films to heavy-duty agricultural and construction films. It is a cost-effective way to produce large volumes of film with consistent quality and can be customized to meet specific customer requirements.
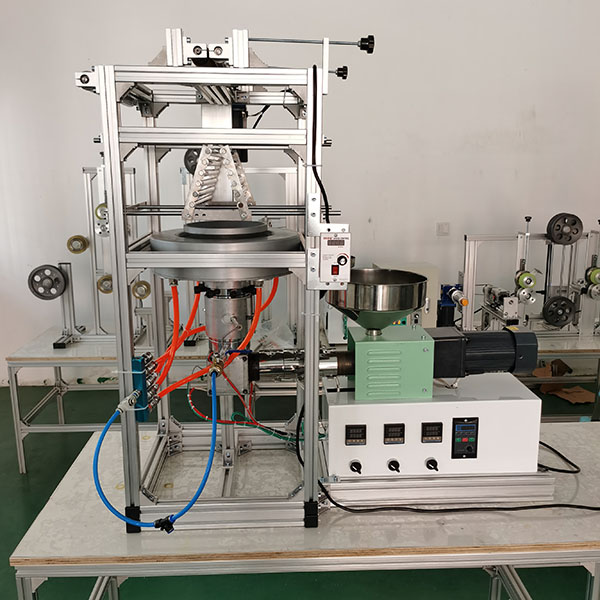

Operation manual of the Desket-FB35 Film Blown Experimental Production
If you already have the SJ25 or SJ35 extruder, you will need a mold for the Die Nozzle, as well as the subsidiary equipment.
Desket-FB_Simple is an SJ35 extruder with a film-blown mold for the experiment of plastic film-blowing purposes without any auxiliary parts (Blown Film Air Ring, the film tower frame, and the winding unit).
Two-layer or three-layer film blown coextrusion
Cast film, film calendering
Film casting is a technique used to produce thin films of polymer material, typically used in packaging, food wrapping, or other applications requiring barrier properties. The process involves heating a polymer resin to a certain temperature and then spreading it onto a flat surface, usually, a metal drum or an endless belt, using a die or a slot die extruder. The polymer film is then cooled, either by air or water, to solidify and maintain its shape.
Cast film experiment extrusion line
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1s93BxZKvskfITYPYUIQVfzFQmAc_u6PU/view?usp=sharing
During the process, the thickness of the film is controlled by the gap between the die and the surface, as well as by the speed at which the surface is moving. The temperature of the polymer melt and the cooling rate also affect the final properties of the film, such as its tensile strength, clarity, and barrier properties.
Film casting is a versatile method that can produce films of different thicknesses, widths, and lengths, as well as films with varying properties. It is widely used in the packaging industry, where it provides a cost-effective solution for producing films with good barrier properties, such as oxygen, moisture, and light.
When we talk about "film casting" you may think it's to make a video/film, no way! Film casting is for the plastic film, which is widely found in our daily life for packaging, etc, which involves the extrusion of polymers melted through a flat die to form a thin film or plate.
Melt Blown Experimental Line
PP or PU melt-blown experiment lab extruder SJ35 and its auxiliary.
SJ15 Melt-blown experiment line
Screw Diameter: 15 mm
Designed Output: 0.01-0.8 kg/h
Machine Dimensions: 1.5 x 0.2 x 0.4 m
Extrusion Center Height: 300 mm
Extrusion Direction: Right to left
Motor Power: 200 W
Voltage: 220 V (or customize)
L/D Ratio: 28:1
Heating Temperature: Room temperature up to 350°C
Feeding Zone: Features a silent cooling device
Screw and Barrel Material: 38CrMoAl, nitrided
Heating Zones: 5
Melt-blown Width: 10-200 mm, adjustable
Winding Speed: Adjustable
Melt blown extrusion is a process used to produce melt blown fabric, which is a type of non-woven fabric consisting of very fine, randomly arranged fibers. The process involves melting a polymer resin, usually polypropylene, and extruding it through a spinneret with tiny holes. The polymer streams are then subjected to high-velocity air jets that draw out the streams into fine filaments that are collected on a conveyor belt or a drum. The filaments are then bonded together to form the final fabric.
The key to melt-blown extrusion is the use of high-velocity air jets, which create turbulence in the polymer streams as they are extruded. This turbulence causes the streams to stretch and break up into many small filaments, which are then collected and bonded together to form the final fabric. The size of the spinneret holes, as well as the air pressure and temperature, can be adjusted to control the diameter and length of the filaments, which in turn affects the properties of the final fabric.
Melt blown fabric is widely used in various applications, such as filtration, medical textiles, and environmental protection, due to its high filtration efficiency, low-pressure drop, and good air permeability.
PVDF film casting or calendering
1. You may study from Google or Wikimedia that PVDF particles are difficult to form films by themselves. If you want to make PVDF particles into a film, you must add about 30% polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA for short, commonly known as acrylic) as a plasticizer to improve its film-forming properties. PVDF after adding PMMA Film formation is easier in the molten state.
So you may need to do modifications firstly with a pelletizing line.
2. Melt-blown is not for film but for plastic coating like non-woven fabric. Film-blown processing is usually for at least two layers of films which are for bags or so. Regarding the film-forming process of PVDF films, the market is dominated by two forming processes: film blowing and casting. However, the cast PVDF film has more advantages in parameters such as light transmittance and thickness uniformity. The PVDF cast film production line has become The current mainstream development direction.
3. Desket-FC35 is the right film casting line for an experimental film, which is cost-performance, and with less material input.
Extrusion Blow Molding
How it works:
Extrusion: Plastic resin is melted and extruded through a die, forming the parison.
Molding: The mold closes around the parison.
Inflation: Compressed air is injected, inflating the parison.
Cooling: The plastic cools and solidifies.
Ejection: The mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
Where it's used:
Packaging industry (bottles, containers)
Automotive industry (fuel tanks, ducts)
Toy manufacturing
And many other industries that require hollow plastic parts.











